MOLECULAR STRUCTURE, QUANTUM-CHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND SPECTRAL PROPERTIES HALOGEN CONTAINED DIMERS OF BENZENE
СУЧАСНЕ МАТЕРІАЛОЗНАВСТВО ТА ТОВАРОЗНАВСТВО: ТЕОРІЯ, ПРАКТИКА, ОСВІТА :: Актуальні питання наукового та практичного матеріалознавства.
Сторінка 1 з 1
 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE, QUANTUM-CHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND SPECTRAL PROPERTIES HALOGEN CONTAINED DIMERS OF BENZENE
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE, QUANTUM-CHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND SPECTRAL PROPERTIES HALOGEN CONTAINED DIMERS OF BENZENE
Korotkova I. V., Docent Department of Common and Biological Chemistry,
Poltava State Agrarian Academy
Poltava State Agrarian Academy
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE, QUANTUM-CHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND SPECTRAL PROPERTIES HALOGEN CONTAINED DIMERS OF BENZENE
In condensed medium many of an aromatic molecules in the ground state can form dimers and aggregates of different types, that in some cases a significantly effect on their spectral-luminescent properties and complicate the industrial application of such molecular systems. The problem of dimer formation and establishment of dimer structures have been drawn much attention and large number of publications was appeared in the recently literature [1-3]. In particular for benzene this problem was investigated in the last decades both experimentally and theoretically. Scheme of dimer configurations for benzene molecules have been proposed. The mathematical relationships for calculating the configuration and energy characteristics of dimers: the equilibrium distance between the centers of mass of particles in the dimers were obtained [4]. However, until now, the methods of the description of structure and spectral properties of halogen contained dimers of benzene are developed not enough despite the fact that these materials are considered as a perspective material for molecular electronics, for applications in the area of materials science and various photonic technologies [5].
The present communication deals with the investigation of the structural and spectroscopic investigation of monomeric and dimeric forms of halogen-contained benzene. It is well-known that the spectral methods occupy the central place among the arsenal of methods to obtain information about the dimers. They are associated primarily with the treatment of the emission spectra of dimers. At the present time the methods of quantum-chemical calculations of the parameters of dimers successfully developed. These methods cannot compete with spectroscopic methods on accuracy and reliability. However, this trend is progressing rapidly and its opportunity is changing. In the present study the quantum-chemical calculations of electronic parameters of the para-dichlorobenzene, para-dibromobenzene as possible dimer formation systems were carried out by TD-DFT method with the B3LYP functional and the 6-31G basis set. It is well known that the spectral properties of aryl systems are sensitive to conformational changes. First of all, the dependence of the total energy of the monomers dibromobenzene, dichlorobenzene as a function of the bond lengths of Ph-Br (1,86-1,95 Å) and Ph-Cl (1,64-1,75 Å) (Fig. a, b) was analyses. On the base of the graphically dependence we concluded that the bond length of 1,86 Å and 1,7 Å, respectively, corresponds to the most stable structure of monomers.
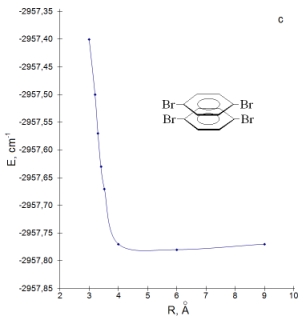
All model dimers were constructed on the basis of this geometry. We have calculated the absorption spectra different model systems of dimers as a function of the distance between monomers and the angle rotation of monomer. We have considered rotation one of the monomers in dimer and constructed the corresponding total energy as a function of the rotation angle defined with respect to the most stable dimers configuration. As follow from calculation results, the increasing of distance between monomers from 3 to 9 Å leads to an increasing the energy of lowest-lying singlet level on 1600 cm-1 and lowest-lying triplet level on 614 cm-1 in the dimer of p-DBrPh. The total energy of the dimer system have a minimum at R=6 Å (Fig. c).
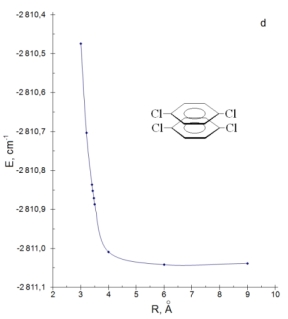
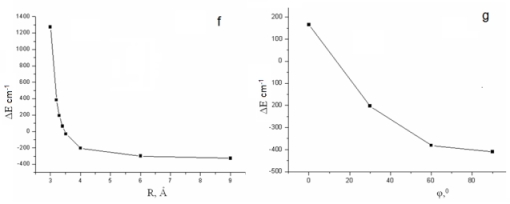
The dimer formation of p-DClPh is characterized by a bathochromic shift of 0-0 transition band on 911 cm-1 at R=3 Å. The hypsochromic shift of the same value is observed when the distance between monomers was increased to 9 Å. The total energy of the dimer system have a minimum in a point which corresponds to R=6 Å (Fig. d). To clarify the geometry of the dimers we have also investigated the dependence of ΔE (ES1 monomer - ES1 dimer) on the distance between the monomers and the angle of rotation of the monomer. The previously experimental studies indicated that the absorption spectra of the crystalline forms of p-DBrPh and p-DClPh bathochromic shifted relative to the spectra in the gaseous phase on 177 cm-1 and 92 cm-1 respectively [6]. On the base of calculation results we found that for p-DBrPh dimer the value of E=177 cm-1 can be due to structure with distance between molecules of 3,32 Å (Fig. f) and in which one of molecules is parallel to another (angle of rotation is 00, Fig. g).
The similar dependences were investigated for the dimer of p-DClPh. The rotation of monomer at R=3 Å changes of E from 900 cm-1 to 300 cm-1, but not decreases to experimental value on 93 cm-1. Really, the correspondence to the experimental value of 93 cm-1 can be achieved in structure of dimer in which two molecules are arranged parallel to each other at distance of 3.48 Å and angle of 250.
In general, a good agreement between available experimental and calculated spectral parameters of investigating dimers has been observed. The result of the current study may give useful information about the spectroscopic properties of halogen-contained benzene systems based on the quantum-chemical data at different structural parameters and in this way the study on the structural features of analogous molecules of condensed aryl systems would be possible.
1. Xie L.-F., Ye C.-C., Ju X.-H., Zhao F.-Q.// Журн.структ.химии. - 2012. - Т.53, № 4. – С.672-678. 2. Бабин Ю. В. // Журн. физ.химии. - 2008. - Т. 82, № 1. - С. 104-111. Sinha L., Prasad O., Karabacak M., Mishra H.N., Narayan V., Asiri AM.//Spectrochim. аcta. A. - 2014. – 120. – P.126-136. 3. Мельников Г. А., Вервейко В. Н., Ларионов А. Н. // Вестн. ВГУ. Серия: Физика. Математика. - 2012. - № 1. - С. 42-51. 4. Zorky P.M., Grinyova O.V. //J. of Struc. Chemistry. - 2001. – 42. - N1. - P.21-30. 5. Klimusheva G.V., Yaremko R.V.// Optika i Spektroskopiya. - 1971. – 31. – P. 234-238.
The present communication deals with the investigation of the structural and spectroscopic investigation of monomeric and dimeric forms of halogen-contained benzene. It is well-known that the spectral methods occupy the central place among the arsenal of methods to obtain information about the dimers. They are associated primarily with the treatment of the emission spectra of dimers. At the present time the methods of quantum-chemical calculations of the parameters of dimers successfully developed. These methods cannot compete with spectroscopic methods on accuracy and reliability. However, this trend is progressing rapidly and its opportunity is changing. In the present study the quantum-chemical calculations of electronic parameters of the para-dichlorobenzene, para-dibromobenzene as possible dimer formation systems were carried out by TD-DFT method with the B3LYP functional and the 6-31G basis set. It is well known that the spectral properties of aryl systems are sensitive to conformational changes. First of all, the dependence of the total energy of the monomers dibromobenzene, dichlorobenzene as a function of the bond lengths of Ph-Br (1,86-1,95 Å) and Ph-Cl (1,64-1,75 Å) (Fig. a, b) was analyses. On the base of the graphically dependence we concluded that the bond length of 1,86 Å and 1,7 Å, respectively, corresponds to the most stable structure of monomers.
All model dimers were constructed on the basis of this geometry. We have calculated the absorption spectra different model systems of dimers as a function of the distance between monomers and the angle rotation of monomer. We have considered rotation one of the monomers in dimer and constructed the corresponding total energy as a function of the rotation angle defined with respect to the most stable dimers configuration. As follow from calculation results, the increasing of distance between monomers from 3 to 9 Å leads to an increasing the energy of lowest-lying singlet level on 1600 cm-1 and lowest-lying triplet level on 614 cm-1 in the dimer of p-DBrPh. The total energy of the dimer system have a minimum at R=6 Å (Fig. c).
The dimer formation of p-DClPh is characterized by a bathochromic shift of 0-0 transition band on 911 cm-1 at R=3 Å. The hypsochromic shift of the same value is observed when the distance between monomers was increased to 9 Å. The total energy of the dimer system have a minimum in a point which corresponds to R=6 Å (Fig. d). To clarify the geometry of the dimers we have also investigated the dependence of ΔE (ES1 monomer - ES1 dimer) on the distance between the monomers and the angle of rotation of the monomer. The previously experimental studies indicated that the absorption spectra of the crystalline forms of p-DBrPh and p-DClPh bathochromic shifted relative to the spectra in the gaseous phase on 177 cm-1 and 92 cm-1 respectively [6]. On the base of calculation results we found that for p-DBrPh dimer the value of E=177 cm-1 can be due to structure with distance between molecules of 3,32 Å (Fig. f) and in which one of molecules is parallel to another (angle of rotation is 00, Fig. g).
The similar dependences were investigated for the dimer of p-DClPh. The rotation of monomer at R=3 Å changes of E from 900 cm-1 to 300 cm-1, but not decreases to experimental value on 93 cm-1. Really, the correspondence to the experimental value of 93 cm-1 can be achieved in structure of dimer in which two molecules are arranged parallel to each other at distance of 3.48 Å and angle of 250.
In general, a good agreement between available experimental and calculated spectral parameters of investigating dimers has been observed. The result of the current study may give useful information about the spectroscopic properties of halogen-contained benzene systems based on the quantum-chemical data at different structural parameters and in this way the study on the structural features of analogous molecules of condensed aryl systems would be possible.
1. Xie L.-F., Ye C.-C., Ju X.-H., Zhao F.-Q.// Журн.структ.химии. - 2012. - Т.53, № 4. – С.672-678. 2. Бабин Ю. В. // Журн. физ.химии. - 2008. - Т. 82, № 1. - С. 104-111. Sinha L., Prasad O., Karabacak M., Mishra H.N., Narayan V., Asiri AM.//Spectrochim. аcta. A. - 2014. – 120. – P.126-136. 3. Мельников Г. А., Вервейко В. Н., Ларионов А. Н. // Вестн. ВГУ. Серия: Физика. Математика. - 2012. - № 1. - С. 42-51. 4. Zorky P.M., Grinyova O.V. //J. of Struc. Chemistry. - 2001. – 42. - N1. - P.21-30. 5. Klimusheva G.V., Yaremko R.V.// Optika i Spektroskopiya. - 1971. – 31. – P. 234-238.
СУЧАСНЕ МАТЕРІАЛОЗНАВСТВО ТА ТОВАРОЗНАВСТВО: ТЕОРІЯ, ПРАКТИКА, ОСВІТА :: Актуальні питання наукового та практичного матеріалознавства.
Сторінка 1 з 1
Права доступу до цього форуму
Ви не можете відповідати на теми у цьому форумі